Sewage treatment plants play a critical role in managing wastewater and protecting both public health and the environment. As urban populations grow and water usage increases, treating sewage properly has become essential to prevent pollution and ensure sustainable water management. Understanding the importance, stages, and methods of sewage treatment plants helps industries, municipalities, and communities make informed decisions about wastewater handling.
Table of Contents
ToggleImportance of Sewage Treatment Plants

The primary purpose of a sewage treatment plant is to remove contaminants from wastewater before it is discharged back into nature or reused. Untreated sewage contains harmful bacteria, organic waste, chemicals, and suspended solids that can pollute rivers, lakes, and groundwater. For large-scale facilities and commercial projects, installing a professionally designed sewage treatment plant ensures long-term wastewater control and environmental compliance.
Proper sewage treatment helps:
- Protect drinking water sources from contamination
- Reduce the spread of waterborne diseases
- Prevent environmental damage to aquatic ecosystems
- Support safe water reuse for irrigation and industrial purposes
Without effective sewage treatment, wastewater can become a serious health and environmental hazard.
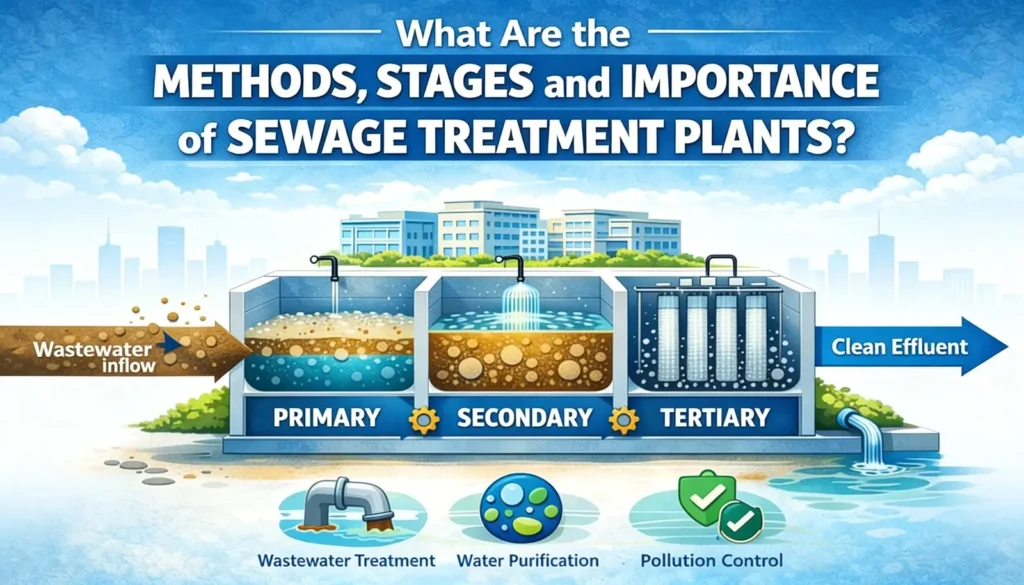
Stages of Sewage Treatment Plants
Sewage treatment is carried out in multiple stages, each designed to remove specific types of contaminants.
Preliminary Treatment
This is the first step, where large solids, debris, and grit are removed using screens and grit chambers. This stage protects downstream equipment from damage.
Primary Treatment
In primary treatment, wastewater is allowed to settle in sedimentation tanks. Heavy solids sink to the bottom as sludge, while lighter materials float to the surface and are removed.
Secondary Treatment
This stage focuses on biological treatment. Microorganisms break down organic matter in the wastewater using processes such as activated sludge or biofilm systems. Secondary treatment significantly reduces organic pollution.
Tertiary Treatment
Also known as advanced treatment, this stage further purifies the water by removing remaining nutrients, pathogens, and fine particles. Filtration and disinfection are commonly used here.
Methods of Sewage Treatment
Different sewage treatment methods are used depending on capacity, wastewater quality, and regulatory requirements.
Activated Sludge Process
This is one of the most widely used methods. It relies on aeration tanks where microorganisms consume organic pollutants.
Trickling Filters
In this method, wastewater passes over a bed of media coated with bacteria that break down organic matter naturally.
Membrane-Based Treatment
Advanced systems use membranes to physically separate solids and microorganisms, producing high-quality treated water suitable for reuse.
Natural Treatment Systems
Lagoons and constructed wetlands use natural biological processes to treat sewage with lower operational costs, though they require more space.
Choosing the Right Sewage Treatment Approach

Selecting the right sewage treatment plant depends on factors such as wastewater volume, treatment goals, land availability, and operational costs. A well-designed system ensures long-term efficiency, regulatory compliance, and environmental safety. Modern industries increasingly rely on advanced water treatment systems to manage sewage efficiently while reducing environmental impact. If you need expert guidance on selecting or upgrading a sewage treatment system, feel free to contact our team for professional support.
FAQs
1. Why are sewage treatment plants important?
They protect public health and the environment by removing harmful pollutants from wastewater before discharge or reuse.
2. What are the main stages of a sewage treatment plant?
The main stages are preliminary, primary, secondary, and tertiary treatment.
3. Which sewage treatment method is most effective?
There is no single best method. Effectiveness depends on wastewater type, treatment goals, and operational requirements.
4. Can treated sewage water be reused?
Yes, treated sewage water can be reused for irrigation, industrial processes, and non-potable applications after proper treatment.
5. What happens to sludge produced during treatment?
Sludge is further treated through digestion, dewatering, and safe disposal or reuse, depending on regulations.